Step-by-step Applications
These simple models are presented as an introduction to the GreatMod usage, showing step by step the base functionalities of the R package, epimod.
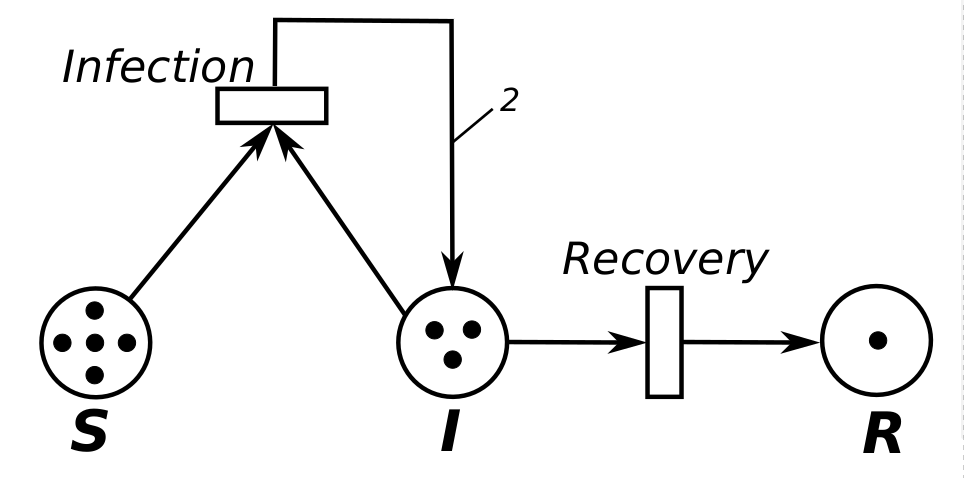
SIR
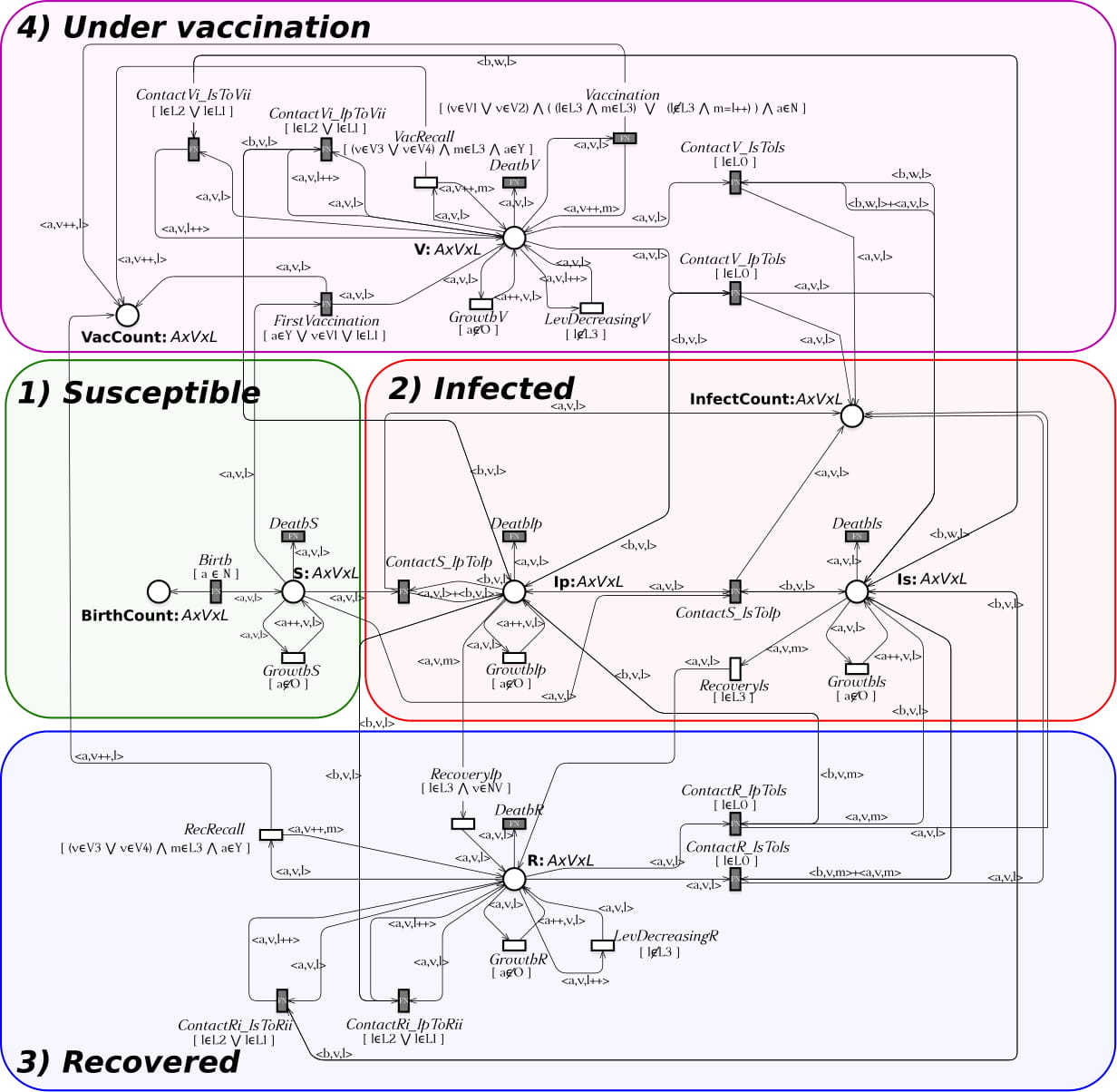
The SIR model is one of the simplest compartmental models, and many models are derivatives of this basic form. The model consists of three compartments: S for the number of susceptible, I for the number of infectious, and R for the number of recovered or deceased.
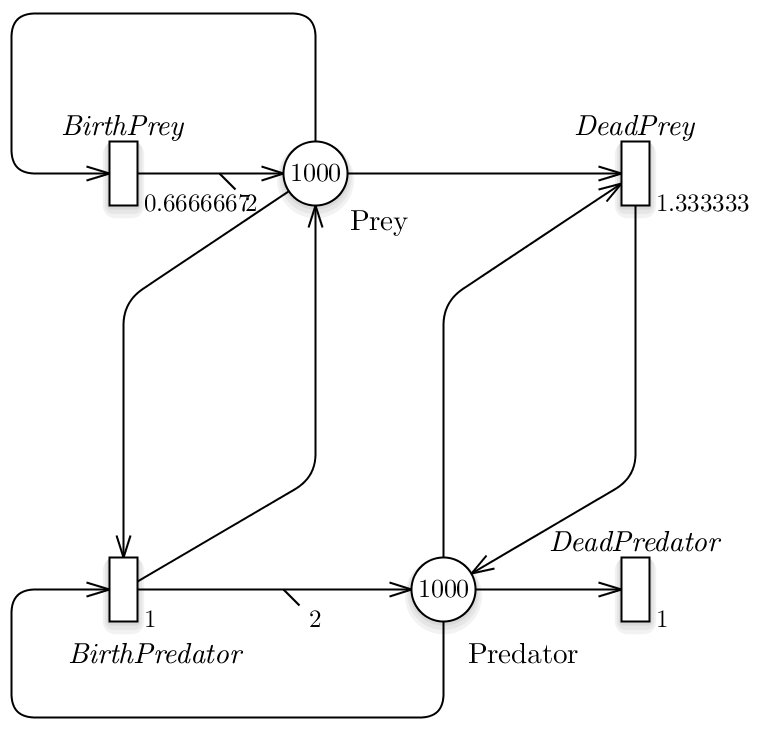
Lotka Volterra
The Lotka–Volterra equations, also known as the predator–prey equations, are a pair of first-order nonlinear differential equations, frequently used to describe the dynamics of biological systems in which two species interact, one as a predator and the other as prey.
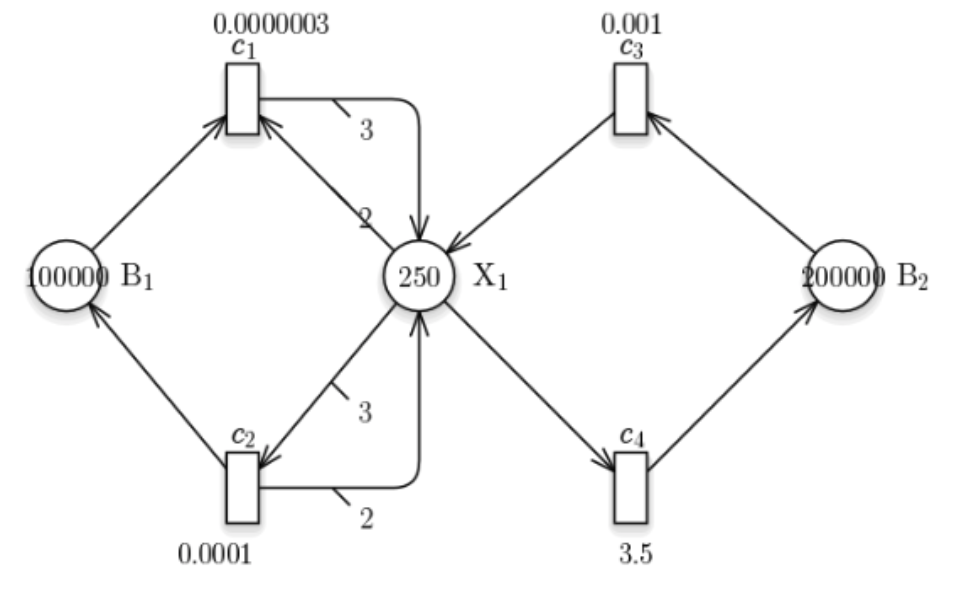
Schlogl model
The Schlogl model was conceived for modeling and simulation of biochemical systems. The Schlogl model depends exclusively on the chemical species X1 with a peculiar features such as bistability and first order phase transition (energy-assisted jumps between states), and front propagation in spatially extended systems.
Complex Applications
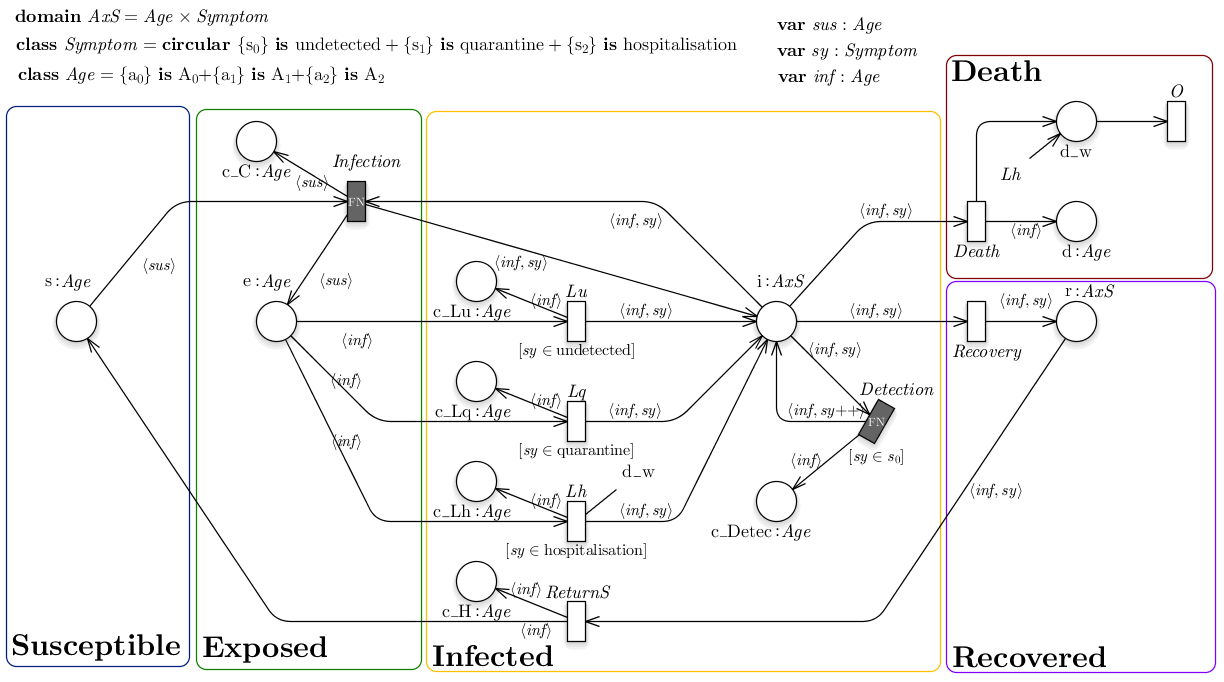
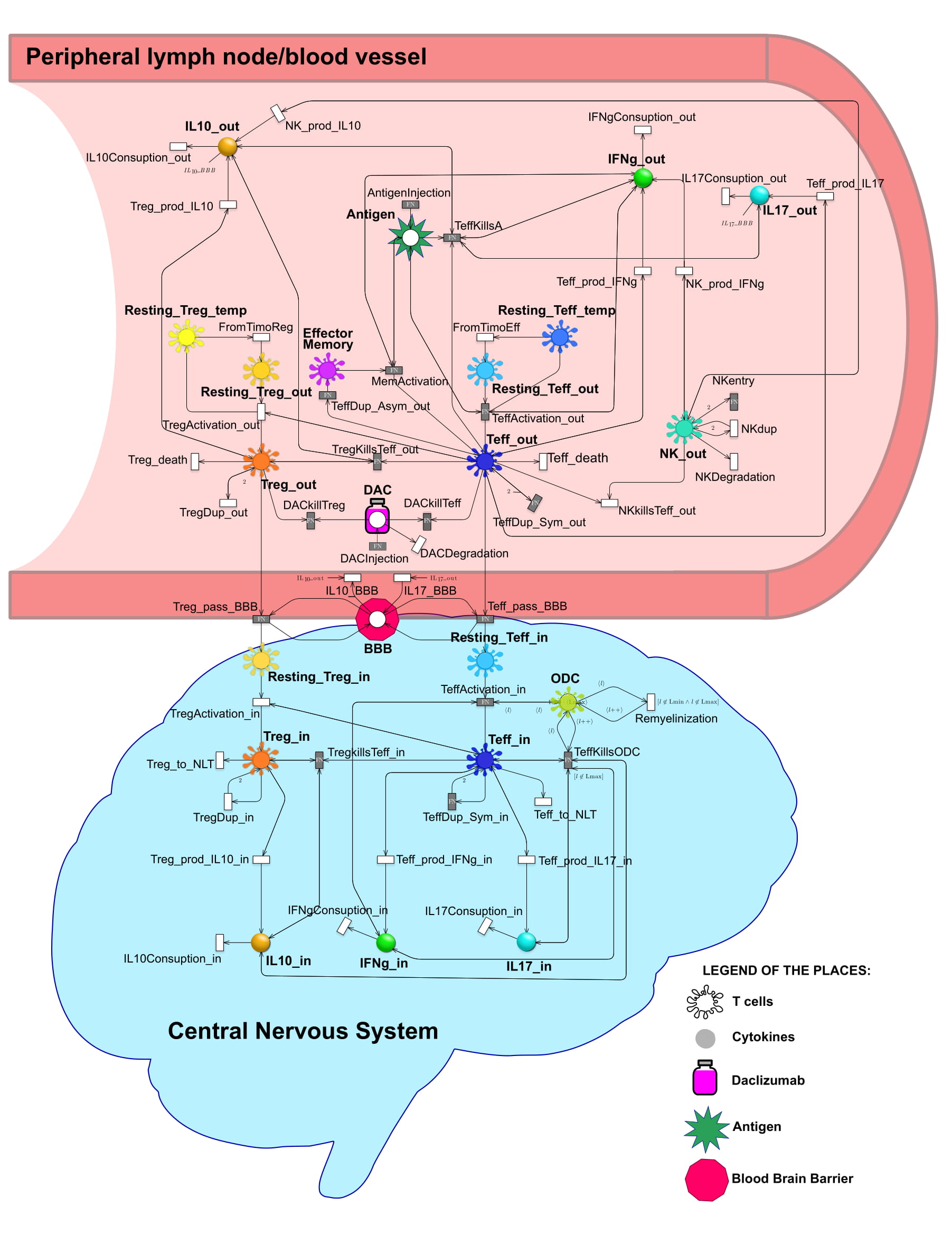
Multiple Sclerosis
Analysis of the immune response in Multiple Sclerosis given specific treatments